What Different Kinds Of Leather Are There?
There are many different kinds of leather around today, the four main types of Pigmented Leather, Nappa Leather, Aniline Leather and Semi Aniline Leather.
Some leather resellers use other terms for leather hides and this can be confusing for the public if they don’t know about leather.
The most common types of leathers are cow hide, sheep skin and goat hide.
Below are just a small selection of the types of leather available.
FULL ANILINE
The most attractive and natural leathers which are prized for their soft natural feel. These are leathers which have been aniline dyed in a vat process with no colour coating added to the surface. They are the most expensive leathers to produce because only the very best selection of hides can be used to produce full aniline leathers. Full aniline dyed leathers are more susceptible to absorbing liquids because of the natural porosity of the hide. Because they don’t have a top coating the leather breathes more easily and is cooler to sit on.
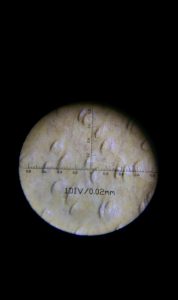
Aniline Leather Through A Microscope
This is aniline leather through a microscope using a powerful 100x micrscope look carefully at the structure and how it looks natural.
PULL UP ANILINE
This is a type of aniline leather (described above) that has an extra top treatment of oil and/or wax effects. These Pull Up leathers are designed to become “distressed” looking through time and use. Its properties are similar to full aniline but in places of heavy use, the oils will be pushed away leaving lighter areas – particularly on the seating areas. It will also scratch easily. The Leather Repair Company has special products designed to restore the look and feel of Pull Up leathers.
SEMI-ANILINE
Semi-Aniline dyed leathers have been both dyed through and have a thin finishing layer on the surface. They offer a combination of the softness and feel of full aniline leather with the protective benefits of a surface finish. By dyeing the leather through before the final thin top coating is applied, a very even colouration is achieved with only a thin layer of finish. This means the leather remains softer because it is not necessary to apply a thick top coating.
PIGMENTED
The leather may be buffed (corrected) to reduce heavy natural scarring and blemishes in the hides. It is then coloured with a coating containing opaque pigments and embossed with a grain pattern to ensure a uniformity of colour and resistance to fading.

Pigmented Leather Through A Microscope
This is pigmented leather this is self-explanatory it’s coated in a colour, filling in the grain pattern making it look smooth and plastic looking.
NUBUCK: also called – CHAPS, STONEWASHED OR SUEDE
These are actually aniline leathers where the surface has been brushed, and have created a texture similar to a velvet on leather. Many people confuse these with suede leather. Suede is the flesh side of a piece of leather, and nubuck is an effect that is done to the grain side. This brushing actually breaks the surface and opens up the leather even more making it incredibly soft. The brushing also makes the leather even more absorbent than aniline leathers.
Shearlings
A generic name given for the wool skins used mostly in the garment industry as the fur is on the grain side the most effective finish is suede, but most finishes can be applied to the flesh side. For this item prices are high currently due to a strong demand and low kills.
Nappa
There are various finishes on Nappa, but this is a generic name given to the grain side finish of Lamb and Cow hides, this type of product is the most widely used for all aspects of the leather industry. Nappa normally has a smooth surface. Methods such as washing or shrinking are then applied after the skin has been through all the previous steps and processes of tanning.
Vegetable Tanned
Vegetable tanning is probably the most talked about as being safe and bio friendly and very kind to the environment. Vegetable tanning is probably the most traditional way of tanning hides. This is all done by using Italian artisans, most of the process is actually done by hand also making it a truly handmade product. Unlike chrome tanning, vegetable tanning can take up to 120 days to produce a piece of dyed leather.

Veg Tanned Leather Through A Microscope
This is veg tanned leather, its natural, again its dyed using vegetable matter like bark extracts etc. This is a full grain veg tanned leather sample, used a great deal in the handbag and luxury goods market.
Crust Leather
Crust leather has been tanned, treated to be non-perishable, but not coloured or otherwise finished in any way. Crust leather are very difficult leathers for cleaning due to them having a zero surface finish or protection. Crust leathers are also known as naked leathers as they are natural and normally top grain leather or full grain leather.
PU Leather
PU leather has a glossy polyurethane coating applied to the surface with a very water resistant coating, its foil coated split leather, its in effect at artificial leather as the split hide is always on the back of the material.
Rub Off leather
Is A Pigmented Finish With The Surface Rubbed Off
Rub off leather is a variety of pigmented leather where the surface is made with more characters by application of a contrasting top coat, which can be partly removed – rubbed off to reveal the underlying colour. This effect relies on a very thin layer, which has very limited durability. This leather will be subject to colour changes when in use.
Split Leather
When manufactured a split is rough on both side, the side nearest to the blade is considered the side to use, the use this gets and finish that’s applied depends on a full inspection of the hide, so it can be a finished split, a coated split (byCast) or a suede split.
A split leather hide is weak in construction, stiffer and prone to cracking compared to normal hides, a split has had a false grain applied and is then pigment coated, used mainly on the sides and backs of furniture, as its a cheaper method of construction.